Flatfoot is common in both children and adults. When this occurs in children, it is referred to as pediatric flatfoot. Although there are various forms of flatfoot, they all share one characteristic – partial or total collapse of the arch. Pediatric flatfoot can be classified as symptomatic or asymptomatic. Symptomatic flatfeet exhibit symptoms such as pain and limitation of activity, while asymptomatic flatfeet show no symptoms.
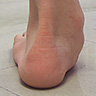
Flatfoot Deformity in a 12 year old patient.
Symptoms
Flatfoot can be apparent at birth or it may not show up until years later. Most children with flatfoot have no symptoms, but some may have the following complaints:
- Pain, tenderness, or cramping in the foot, leg, and/or knee.
- Outward tilting of the heel.
- Awkwardness or changes in walking.
- Difficulty with shoes.
- Reduced energy when participating in physical activities.
- Voluntary withdrawal from physical activities.
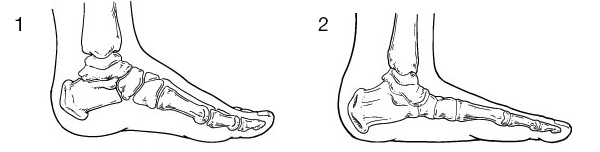
Comparing normal pediatric foot (1) and flatfoot (2).
Why See A Foot Specialist?
In diagnosing flatfoot, the doctor examines the child’s foot and observes how it looks when the child stands and sits. The doctor also observes how the child walks and evaluates the range of motion of the foot.
Because flatfoot is sometimes related to problems in the leg, the doctor may also examine the knees and hips. Depending on the severity of the deformity and symptoms, x-rays may be taken. Sometimes additional imaging and other tests are ordered.
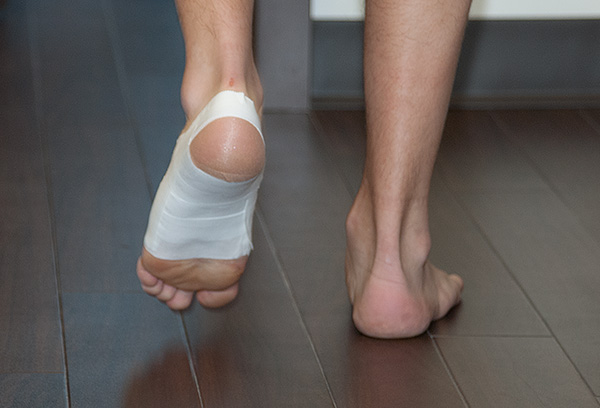
Low dye tape can be applied to provide temporary support to the foot and improve its mechanics.
Treatment
If a child has no symptoms, treatment is often not required. Instead, the condition will be observed and re-evaluated routinely by the doctor. Custom orthotic devices may be considered for some cases of asymptomatic flatfoot, especially if the child is very active. When the child has symptoms, treatment is required. The foot specialist may select one or more of the following non-surgical approaches:
Activity modifications
The child needs to temporarily decrease activities that bring pain as well as avoid prolonged walking or standing.
Orthotic devices
Orthotic device is a custom medical device prescribed by the doctor. It can fit inside the shoe to support the structure of the foot and improve function.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is a series of stretching exercises, strength, and endurance training by a licensed physiotherapist to promote return to activities.
Shoe modifications
Doctor will advise you on footwear characteristics that are important for the child with flatfoot.
Surgery
In rare cases, surgery is necessary to relieve the symptoms and improve foot function. The surgical procedure or combination of procedures selected for your child will depend on his or her type of flatfoot and degree of deformity. This will be determined by the doctor based on clinical and imaging evaluations.
Remember — it is not normal for children to complain of foot pain or to avoid social and physical activities because of problems in their feet. Contact us for a consultation with our doctor if you are concerned regarding your child’s foot health.